GPS From Photos: Step-by-Step Location Discovery Guide
Published on April 29, 2025 • 11 min read
Want to know where a photo was taken? Many photos store GPS data (latitude, longitude, and more) in their metadata, making it easy to find the location - if the data hasn’t been removed. Even without GPS info, visual clues and AI tools can help pinpoint the spot.
Key Takeaways:
- Check Metadata: Use built-in tools on Windows, Mac, or mobile to view photo metadata.
- Use Advanced Tools: Apps like EXIF Tool or PlaceSpotter analyze images for GPS data or visual details.
- Look for Visual Clues: Identify landmarks, architecture, vegetation, or shadows in the photo.
- Leverage AI Tools: Tools like PlaceSpotter analyze patterns to geolocate images without metadata.
Whether you’re organizing travel photos, solving a mystery, or conducting an investigation, combining metadata, visual analysis, and AI tools can help you determine where a photo was taken.
Photo Metadata and GPS Basics
Metadata Fundamentals
Photo metadata acts like a digital ID for your photos, containing details about camera settings, timestamps, and even GPS coordinates [1].
EXIF data often includes:
- Camera model and lens details
- Technical settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO
- Date and time the photo was taken
- GPS coordinates (latitude and longitude)
- Altitude information
Viewing Metadata on Different Devices
Many devices come with built-in tools to check photo metadata, including GPS details. Here's a quick guide for major platforms:
Windows Users
- Right-click the image and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Details" tab.
- Find GPS coordinates under location information [2].
Mac Users
- Open the image in Preview.
- Click the "i" button at the top.
- Select the "GPS" tab in the info panel.
- Alternatively, right-click the image, choose "Get Info", and check the "More Info" section [3].
Mobile Device Access
- iPhone: Open the Photos app, then swipe up or tap the "(i)" icon to view location details.
- Android: Open Google Photos and tap the three-dot menu to see location information [2].
For more detailed insights, advanced tools can help.
Advanced Metadata Tools
If you need deeper analysis, EXIF Tool is a popular choice and works on Windows, Mac, and Linux [2].
To ensure your iPhone photos include GPS data, enable location services for the Camera app. Go to Settings > Privacy > Location Services, then select the Camera app and choose "While Using the App" [4].
Missing GPS data? Common reasons include:
- Location services turned off for the camera app
- Weak GPS signal when the photo was taken
- Metadata stripped by certain sharing platforms
- Device in Airplane mode during capture
To guarantee future photos contain location data, make sure location services are enabled for your camera app. Use sharing methods that retain metadata, such as iMessage, AirDrop, or email [4].
Once metadata is accessible, visual clues can help further pinpoint locations.
10 Minute Tip: How to geolocate from images and videos
:::
Finding Locations Through Visual Details
When metadata isn't available, visual clues in images can help uncover where a photo was taken. By examining specific features, you can narrow down or even pinpoint the location.
Key Location Markers
Photos often contain visual elements that serve as clues:
Architectural Features
- Building styles and materials
- Unique details like window designs or roof shapes
Natural Elements
- Types of vegetation
- Terrain characteristics
- Recognizable natural landmarks
Urban Details
- Street signs and other infrastructure
In addition to these, shadows in photos can provide more information about the location and even the time the picture was taken.
Shadow-Based Location Analysis
Analyzing shadows can reveal both where and when a photo was captured. This method is particularly useful for verifying image origins.
"SunCalc lets users analyze the position of shadows and the sun at any given time and date, at any given location", says Youri van der Weide, an open-source researcher and trainer for Bellingcat [5].
For example, in November 2020, Bellingcat used shadow analysis to geolocate a video in Lisbon, Portugal. By examining the timestamp, sun position, and shadows at 4:31 PM UTC, they identified Avenida da República in Oeiras.
Shadow Analysis Tips
- Look for clear, distinct shadows.
- Estimate the time of day based on shadow length and direction.
- Check for consistent shadow patterns across the image.
- Account for seasonal changes in the sun's position.
This method is precise and effective, as noted by van der Weide:
"The technique can be highly effective in narrowing down a search area, by excluding false positives and establishing in which direction the camera is pointed in a certain frame." [5]
AI Photo Location Tools
Modern AI technology has advanced to the point where it can determine photo locations by analyzing the image itself - no need for GPS metadata. These tools rely on visual clues within the photo to pinpoint locations.
How AI Finds Photo Locations
AI-powered geolocation tools work by examining the image's visual details instead of relying on metadata or other external inputs [6]. They focus on:
- Visual and Environmental Features: Textures, colors, architectural styles, vegetation, and natural landmarks.
- Infrastructure Elements: Building designs, road layouts, and signage.
- Lighting and Shadows: Patterns of light and shadow to infer details about the time and location.
These systems can process over 200,000 images daily [8], analyzing thousands of elements in each image to improve accuracy. A leading example, PlaceSpotter, uses these techniques to provide precise location insights.
PlaceSpotter Guide
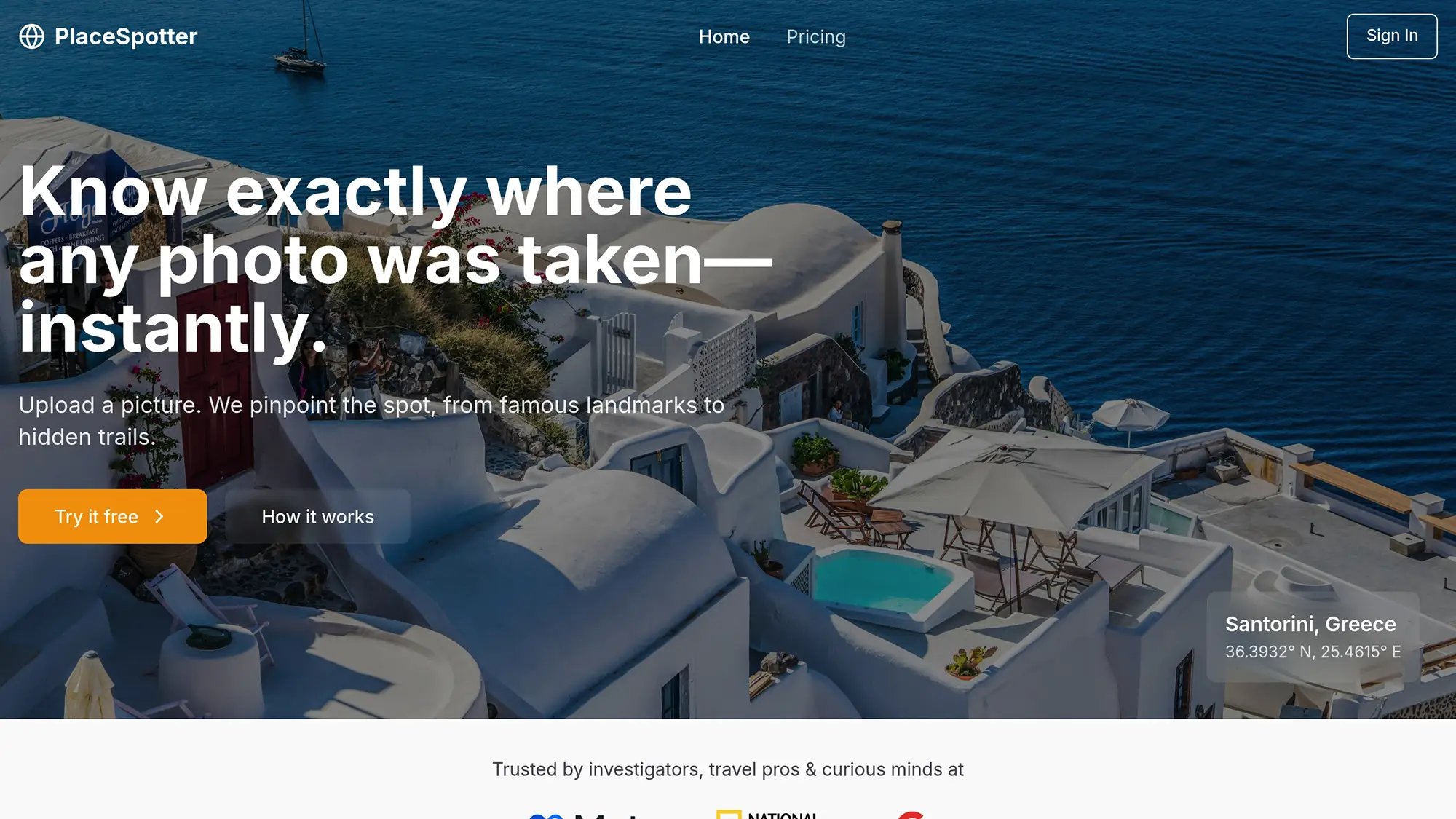
PlaceSpotter showcases how AI can transform visual data into accurate geolocation information. It identifies patterns and matches them to geospatial data for reliable results.
-
Image Selection
Choose photos that include:- Clear views of buildings or landmarks.
- Unique architectural features.
- Visible infrastructure or natural elements like vegetation.
-
Upload Process
Upload high-resolution images in formats like JPEG, PNG, or HEIC. Ensure:- Photos are well-lit.
- Minimal editing has been applied.
-
Location Analysis
Once uploaded, PlaceSpotter’s AI:- Identifies landmarks and infrastructure.
- Analyzes patterns in the image.
- Matches findings with OpenStreetMap data for location accuracy.
| Scene Type | AI Performance |
|---|---|
| Urban Areas | Excellent – plenty of reference points. |
| Landmarks | Very Good – distinct features help. |
| Generic Landscapes | Limited – fewer identifiable elements. |
| Indoor Scenes | Poor – unless unique architecture is visible. |
"From a privacy point of view, your location can be a very sensitive set of information" [7]
While these tools offer impressive functionality, it’s important to consider privacy, especially when analyzing photos that might reveal sensitive or personal details.
Photo Location Process
Identifying where a photo was taken involves combining metadata, visual details, and AI tools. By following a clear process and verifying your findings, you can pinpoint locations with more accuracy.
Steps to Identify a Photo's Location
-
Check Metadata First
Look at the photo's embedded metadata for GPS information and other relevant details. -
Analyze Visual Clues
Examine the photo for:- Architectural styles or unique building features
- Natural landmarks and vegetation
- Street signs, business names, or other text
- Road layouts and infrastructure elements
-
Leverage AI Tools
Use tools like PlaceSpotter to analyze the photo. These tools enhance your findings by combining metadata and visual details with AI-based detection.
Once you've identified a possible location, take extra steps to confirm its accuracy.
Tips for Better Accuracy
Use Multiple Data Points
Cross-check metadata, visual landmarks, and AI results to validate your findings.
Analyze Time Clues
Shadows in the photo can reveal the time of day, which might help narrow down the location.
Look at Seasonal Details
Pay attention to contextual elements like:
- Leaf colors or snow presence
- Weather patterns
- Types of vegetation
Use High-Quality Images
Work with unedited, high-resolution photos (at least 1920x1080) to ensure better detail and improve AI analysis.
If you have several photos from the same area, reviewing them together can help confirm your conclusions.
Common Uses for Photo Location
Travel and Photo Management
GPS data helps organize travel photos and makes it easier to relive trips. Whether you're a professional photographer or a hobbyist, location details simplify photo management and enhance travel documentation.
Organizing Photos Made Simple
With tools like PlaceSpotter, photos can be automatically sorted into location-based albums. This makes finding and managing your images much easier.
Documenting Your Travels
Location data allows you to:
- Track your travel routes
- Pinpoint scenic viewpoints
- Record hidden gems
- Create travel guides with precise locations
This information isn’t just about preserving memories - it can also be used to tackle practical problems.
Finding Lost Items
Location data in photos can be a powerful tool for recovering lost items or aiding investigations. A systematic approach can make all the difference.
Techniques Used by Professionals
Investigators often analyze:
- Landmarks visible in the photo (mountains, buildings, etc.)
- Shadows and time of day
- Clues from the environment (like vegetation or seasonal signs)
"OSINT is about your ability to investigate and interrogate the intelligence you have at hand." - Tiger Catcher, Trace Labs [9]
Combining metadata, visual details, and AI tools can improve accuracy and make investigations more effective.
Tips for Accurate Location Recovery
- Use high-resolution, unedited images
- Take detailed photos of the surrounding area
- Capture multiple angles of the location
- Look for unique landmarks or features
- Leverage AI tools to refine location data
"Remember, good investigators pivot, great investigators correlate and corroborate." - Tiger Catcher, Trace Labs [9]
Conclusion
Finding photo locations involves a mix of careful analysis and leveraging modern tools. This combination forms the foundation of the practices discussed earlier.
Blending Visual Analysis and Technology
Examining landmarks and physical features alongside AI tools like PlaceSpotter can reveal details that might otherwise go unnoticed. These tools complement human observation, offering a more thorough way to pinpoint locations.
Key Steps for Accurate Results
- Check metadata for clues.
- Study visual elements in the photo.
- Use AI tools to confirm findings.
This structured approach helps ensure accurate and reliable location identification by cross-checking multiple data points.
What’s Next for Photo Geolocation?
As technology advances, tools will become even more precise. However, human judgment will always play a crucial role in understanding context and verifying results. Together, these elements provide the most dependable outcomes for identifying photo locations.
With patience, attention to detail, and the right tools, you can uncover the hidden stories behind your photos and their locations.
FAQs
How can I make sure my photos keep their GPS location data when I share them?
To ensure your photos retain GPS metadata when sharing, start by enabling location services on your device. For iPhones, you can confirm a photo is geotagged by swiping up while viewing it - if a map appears, the GPS data is included. On Android devices, you can enable location tagging directly in your camera settings.
Keep in mind that some platforms or apps may automatically strip GPS metadata for privacy reasons when you upload photos. To avoid this, check the platform’s settings or share the photos via methods that preserve metadata, such as email or cloud storage. If needed, you can also use photo editing tools to verify or manage the GPS data before sharing.
What challenges might arise when using AI tools like PlaceSpotter to find a photo's location?
Using AI tools like PlaceSpotter to determine a photo's location can sometimes present challenges. For example, low-quality images or photos without clear, distinguishable features may lead to less accurate results. Additionally, AI tools rely on the availability of data in their databases, so identifying locations in remote areas or regions with limited visual data can be more difficult.
Other challenges include photos of generic landscapes (e.g., forests, deserts) or indoor settings, which often lack unique markers for AI to analyze. While these tools are powerful, their accuracy improves when images are clear and contain identifiable landmarks or features.
How can shadow analysis help identify when and where a photo was taken, and what tools are useful for this?
Shadow analysis is a powerful method for estimating the time and location of a photo by examining the direction and length of shadows relative to the sun. This process, often called chronolocation, can help pinpoint where and when a photo was taken by analyzing the sun’s position in the sky.
Tools like SunCalc allow users to simulate the sun’s path for a specific date, time, and location, making it easier to match shadow patterns in the photo. By combining shadow analysis with other geolocation techniques, you can narrow down the photo’s origin with impressive accuracy.