Manual vs AI Photo Geolocation: Which Method Works Better?
Published on April 30, 2025 • 11 min read
Want to pinpoint where a photo was taken? You have two main options: manual analysis or AI tools. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you choose:
- Manual Geolocation: Relies on human expertise to analyze visual clues (like landmarks, signs, or architecture) and metadata. It’s accurate for complex cases but takes hours and requires specialized knowledge.
- AI Geolocation: Tools like PlaceSpotter use machine learning to compare photos with massive databases of GPS-tagged images. They’re fast, scalable, and work best with clear, high-quality photos.
Quick Comparison
| Method | Speed | Accuracy | Best For | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | Hours to days | High (with expertise) | Complex cases needing detailed analysis | Free but time-intensive |
| AI (PlaceSpotter) | Seconds | High (with clear images) | Large collections or time-sensitive tasks | $4.99–$9.99/month |
Key takeaway: Use AI for speed and bulk tasks, manual methods for precision and unique cases. For the best results, combine both approaches.
Manual Photo Geolocation Methods
Basic Manual Techniques
Manual photo geolocation involves studying visual clues and metadata to figure out where a photo was taken. Analysts typically focus on two main areas:
Visual Analysis
- Architectural styles and building designs
- Traffic flow and types of vehicles
- Natural features like landmarks and vegetation
- Road markings and traffic signs
- Language on signs, flags, or billboards
- Patterns in pedestrian activity
Technical Analysis
- Reviewing EXIF data for embedded details
- Checking GPS coordinates, if available
- Analyzing timestamps for contextual clues
- Examining camera settings and equipment information
A notable example of these techniques in action comes from a case study [2]. Analysts identified a location in Lima, Peru by observing unique features like bus designs and taxi styles typical of South American cities. They confirmed their findings by analyzing the specific patterns on local police uniforms. This example highlights both the precision and the challenges involved in manual geolocation.
Benefits of Manual Analysis
Manual geolocation allows analysts to pick up on subtle cultural or regional details and recognize patterns that automated tools might miss.
Manual Method Drawbacks
While effective, manual analysis comes with some significant challenges:
Time-Intensive Process
- Requires detailed research and multiple verification steps, often taking a long time to complete.
Expertise Is Essential
- Analysts need knowledge of global architecture, cultural indicators, mapping tools, and metadata analysis.
Verification Issues
- Relies on cross-referencing multiple sources, which can lead to confirmation bias.
- Some mapping tools may not provide adequate coverage for certain areas.
The success of manual geolocation depends heavily on the analyst's skills and thoroughness. As emphasized in professional resources [2], carefully examining every detail in an image is critical to avoid errors or misidentifications.
AI Photo Geolocation Systems
AI Geolocation Technology
AI-powered geolocation systems automate and streamline the process of pinpointing locations in photos. Instead of relying on manual analysis, these systems use machine learning to examine visual elements like architectural designs, natural landmarks, vegetation, and infrastructure. Here's how it works:
- Image Analysis: The system scans the image to identify key features.
- Database Comparison: It matches these features against extensive geotagged image databases.
- Location Prediction: Finally, it provides GPS coordinates along with descriptive location details.
PlaceSpotter Features and Tools
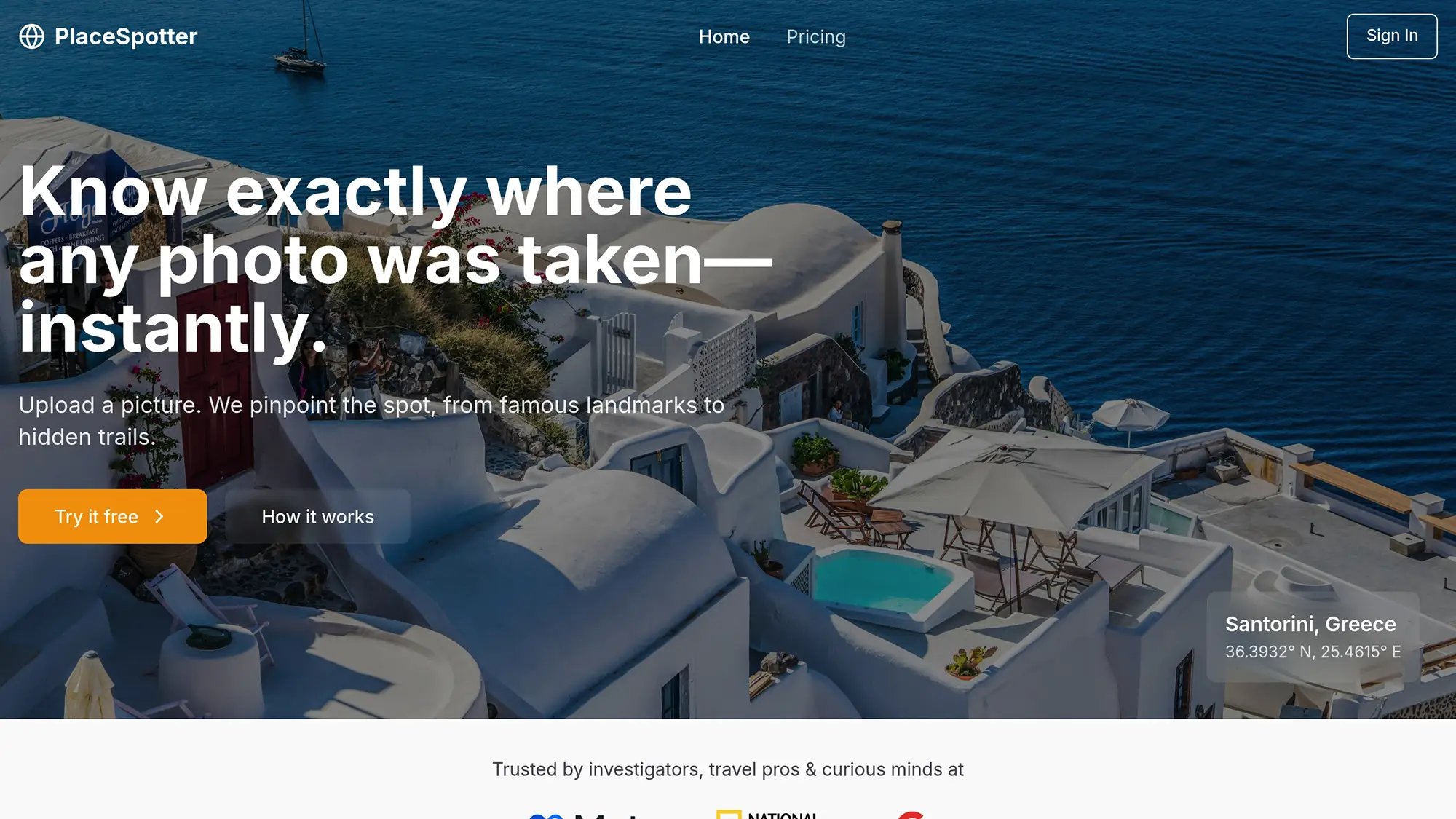
PlaceSpotter leverages cutting-edge AI to deliver accurate location identification. Its tools include:
- Detailed GPS Coordinates: Precise location data for any image.
- Location Name and Map View: Easy-to-understand visual and textual location details.
- Support for Multiple Formats: Handles JPEG, PNG, HEIC, and more.
- Automatic Photo Tagging: Tags images with location data automatically.
- Specialized Workflows: Tailored geolocation processes for specific needs.
PlaceSpotter also offers flexible pricing plans. The Pro plan, priced at $9.99 per month, supports up to 200 photos monthly and includes commercial usage rights. For those looking to test the service, the Free plan allows for 3 photos per month. These plans make it accessible for various users, from hobbyists to professionals.
AI System Benefits
PlaceSpotter demonstrates how AI can transform geolocation with its blend of speed, precision, and adaptability.
Speed and Efficiency
- Processes thousands of image elements simultaneously.
- Delivers location results quickly, cutting down on manual research time.
- Verifies locations in seconds.
Wide Range of Uses
- Confirms the authenticity of news content.
- Tracks the origins of questionable images.
- Assists in missing person investigations.
- Verifies travel photo locations.
Improved Accuracy
- Detects subtle location clues that might be missed by human analysis.
- Handles complex visual patterns with ease.
- Provides dependable location data without needing EXIF metadata.
For the best results, high-quality images with clear and distinct features are recommended. As Jay Stanley from the American Civil Liberties Union notes:
From a privacy point of view, your location can be a very sensitive set of information [3]
Comparing Manual and AI Methods
Location Accuracy Results
AI solutions like PlaceSpotter can deliver results quickly, especially when the conditions - such as image quality and clear landmarks - are ideal. However, their accuracy may vary depending on these factors.
On the other hand, manual geolocation relies on human expertise. Analysts can pick up on subtle details that AI might miss, particularly in challenging scenarios like:
- Generic or nondescript landscapes
- Indoor settings
- Older or degraded images
- Photos with few or no clear landmarks
Research shows that even the most advanced AI systems provide estimates rather than guaranteed pinpoint accuracy [3].
Processing Time Comparison
Here's how manual, AI, and hybrid methods compare in terms of speed and accuracy:
| Method | Processing Time | Accuracy Level | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | Hours to days | High (with expertise) | Complex cases needing in-depth analysis |
| PlaceSpotter AI | Seconds | High (with clear images) | Bulk tasks or time-sensitive needs |
| Hybrid Approach | Minutes to hours | Highest | Critical cases needing verification |
Price and Tool Requirements
Cost and resource demands also play a role when choosing between manual and AI methods. PlaceSpotter offers pricing plans tailored to different levels of usage:
- Free tier: 3 photos per month for casual users
- Lite plan: $4.99/month for up to 30 photos
- Pro plan: $9.99/month for up to 200 photos
- Extra credits: Starting at $2.00 for 10 additional photos
Manual geolocation, while not requiring direct monetary costs, does demand significant time and expertise. It may involve:
- Specialized knowledge of geography
- Access to mapping tools
- Familiarity with regional architecture and landmarks
- Ample time for detailed research and analysis
The decision between manual and AI methods often depends on the specific situation. AI excels in speed and scalability, while human expertise is indispensable for tackling complex cases. Many organizations combine both approaches, using AI for initial screening and manual verification for more critical or nuanced tasks [1].
No Metadata No Problem, Predicting photo locations from ...
Best Uses for Each Method
Here’s how different geolocation methods can be applied effectively in various scenarios.
Photo and Travel Uses
Travel photographers and content creators can take advantage of PlaceSpotter's AI to handle large photo collections with ease. The system is particularly helpful for:
- Tagging and organizing vacation albums: Automatically sorts photos by location.
- Finding hidden spots: Pinpoints exact coordinates of unique locations for future visits.
- Sorting by location data: Keeps photo collections neatly organized based on precise geolocation.
For projects that require a more detailed contextual approach, manual geolocation still plays a key role. Professionals often turn to manual methods when dealing with:
- Historical landmarks with few modern reference points.
- Remote areas featuring distinct architectural features.
- Sites that require a deeper understanding of local context.
These techniques aren’t just for travel - they’re also critical in investigative work.
Research Applications
Manual geolocation is especially valuable in investigations that need human expertise. As osintcombine.com highlights:
"The ability to determine the geographic location of a subject or object from images can be critical in intelligence." [2]
This approach is used to:
- Analyze traffic patterns and pedestrian behavior.
- Identify regional architectural details.
- Interpret cultural markers and local customs.
- Verify locations using a variety of subtle clues.
On the other hand, PlaceSpotter's AI system shines in areas like:
- Processing large photo sets: Quickly analyzes thousands of images.
- Preliminary location identification: Provides fast initial geolocation results.
- Spotting patterns: Identifies subtle visual cues across multiple images.
Business Applications
Businesses have diverse needs when it comes to geolocation, often requiring both speed and accuracy. For organizations managing large-scale image collections - such as media outlets or tourism boards - PlaceSpotter's AI offers fast, scalable solutions that simplify workflows.
In industries where accuracy is paramount, like law enforcement or investigative journalism, a hybrid approach works best. Combining AI’s efficiency with manual review ensures both speed and detailed verification.
Choosing the right method - whether manual, AI-driven, or a mix - depends on the project’s specific goals, the volume of images, and the need for a balance between speed and precision.
Conclusion: Method Selection Guide
Choosing the right geolocation method depends on your specific needs and limitations. Here's a quick guide to help you decide:
| Factor | Go with Manual When | Opt for AI When |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Needs | You need pinpoint accuracy down to exact coordinates | General city or region-level accuracy works |
| Time Available | You can spend hours on detailed analysis | You need results in minutes |
| Image Volume | You’re working with a small number of critical images | You’re processing a large collection of photos |
| Image Features | The images have clear landmarks or distinct architecture | The images lack strong visual reference points |
| Budget | You’re relying on free OSINT tools | You can afford a $4.99–$9.99 monthly subscription |
This table offers a clear breakdown of when each approach works best. For example, PlaceSpotter’s AI is ideal for handling large photo collections under tight deadlines. Travel photographers with hundreds of vacation images can save hours by using automated tagging and sorting.
As noted by osintcombine.com:
"Using AI Systems requires a partnership to get the best results" [2]
This highlights that combining AI and manual methods often delivers the best outcomes. For sensitive investigations or when precision is critical, start with AI-generated suggestions and follow up with manual verification.
For businesses, PlaceSpotter’s automated workflow is perfect for high-volume image processing. On the other hand, investigative journalists may prioritize manual methods for maximum accuracy.
Balancing speed, accuracy, and resources often calls for a hybrid approach, blending AI efficiency with the precision of manual checks.
FAQs
How does AI photo geolocation compare to manual methods in terms of accuracy?
AI-powered photo geolocation tools can analyze images with impressive speed and accuracy, often identifying potential locations in seconds. These tools use advanced technologies like machine learning and reverse image search, making them ideal for quickly narrowing down possibilities. However, they may occasionally produce inaccurate results, especially in cases with minimal visual clues or ambiguous data.
Manual geolocation methods, such as examining landmarks or metadata, often require more time and effort but allow for greater human judgment and context-awareness. In many scenarios, combining AI tools with manual techniques provides the best balance of efficiency and accuracy, especially for tasks like investigative research or travel photography.
How do I decide between manual and AI-powered photo geolocation for my project?
Choosing between manual and AI-powered photo geolocation depends on your project's goals and the resources available. Manual methods involve examining visual landmarks, metadata, and other details to identify a location. This approach can be highly accurate for projects requiring human judgment, such as historical research or detailed image analysis.
On the other hand, AI-powered tools use machine learning to analyze patterns and subtle clues in images that might be difficult for humans to detect. These tools are ideal for tasks requiring speed and scalability, such as processing large volumes of photos or investigative work.
Consider factors like the size of your dataset, the complexity of the geolocation task, and the level of precision needed to determine the best approach for your project.
Can AI tools like PlaceSpotter deliver accurate results for sensitive investigations or cases requiring precise geolocation?
AI-powered geolocation tools, like PlaceSpotter, can be highly effective for identifying potential locations quickly and efficiently. These tools use advanced machine learning and image analysis to provide location estimates based on visual and metadata clues. However, for sensitive investigations or cases requiring exact precision, human expertise often plays a critical role in verifying and refining the results.
While AI can narrow down possibilities and save time, it’s important to combine its insights with manual analysis to ensure accuracy - especially in high-stakes scenarios. This hybrid approach ensures that both the speed of AI and the critical thinking of human expertise are utilized effectively.