FAQ: Finding Exact Locations from Travel Photos
Published on May 12, 2025 • 10 min read
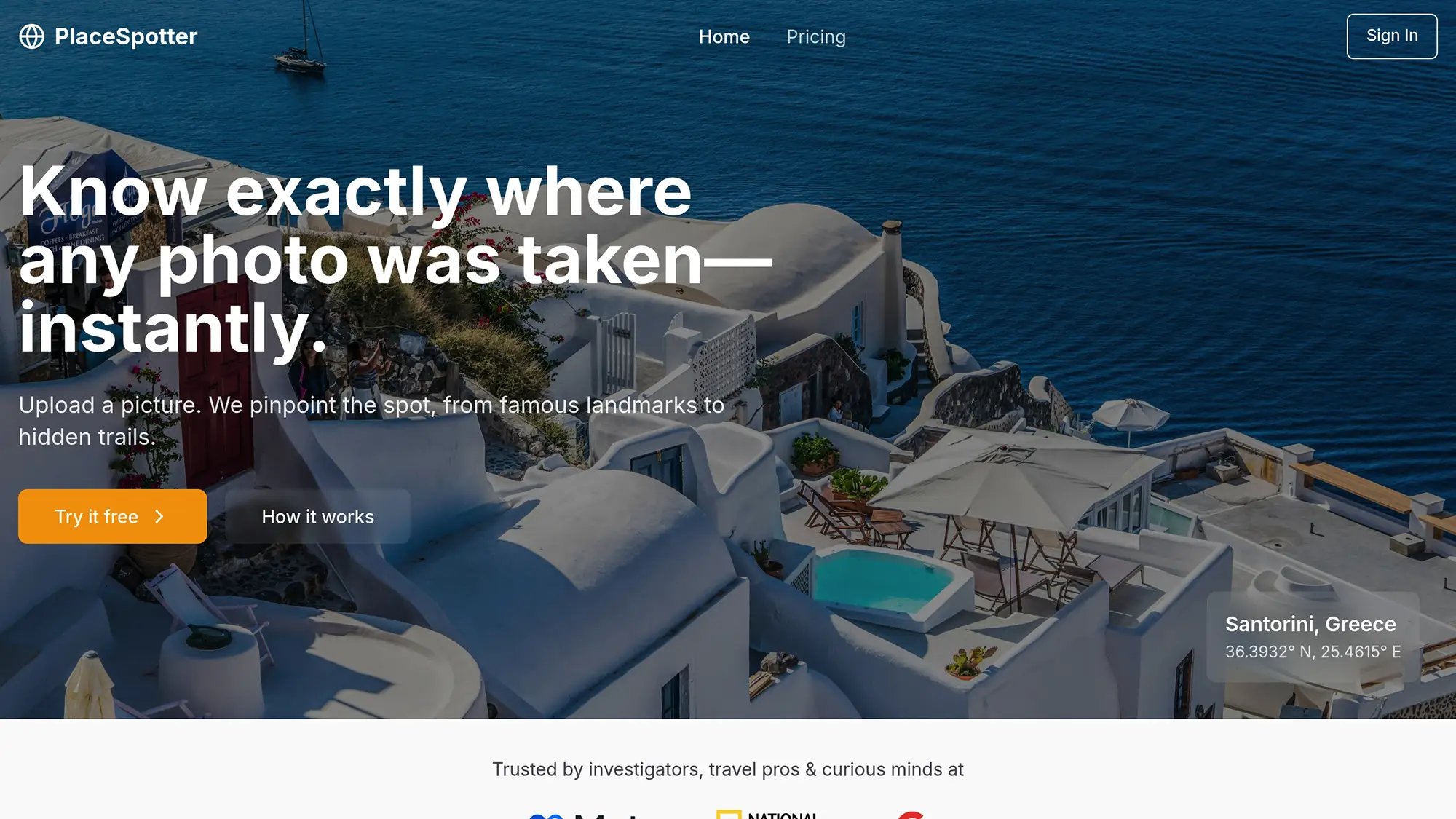
Ever wondered where a photo was taken? AI tools like PlaceSpotter can identify photo locations in seconds by analyzing visual elements (landmarks, architecture, landscapes) and metadata (GPS, timestamps). Here's what you need to know:
- How It Works: Combines visual analysis (e.g., street signs, natural features) with metadata processing (GPS, timestamps) for precise results.
- Privacy: Ensures secure processing and deletes files after analysis.
- Plans: Free (3 photos/month), Lite ($4.99/month, 30 photos), Pro ($9.99/month, 200 photos), or pay-per-use credits.
- Use Cases: Travel logs, photography planning, research, and investigations.
Quick Tip: To improve accuracy, use clear, focused photos with visible landmarks and ensure metadata is intact. Always prioritize privacy by removing geotags before sharing online.
How good are AI Tools at finding locations from photos?
How AI Photo Location Tools Work
PlaceSpotter identifies locations in photos by combining visual analysis with metadata processing. This dual approach creates a detailed location profile. Here's a closer look at the visual elements and metadata that make this possible.
Photo Elements That Help Identify Locations
PlaceSpotter examines several visual details to determine where a photo was taken:
- Architectural Features: Recognizes building styles and structures typical of specific regions.
- Natural Elements: Analyzes landscapes, vegetation, and geological features for location context.
- Urban Infrastructure: Identifies street signs, traffic signals, and public transport markers with local details.
- Commercial Signage: Looks for business names, ads, and branding to narrow down neighborhoods or streets.
"We use a combination of AI visual analysis, landmark recognition, and metadata processing to identify locations with high accuracy." - PlaceSpotter [1]
How Metadata Plays a Role
Photo metadata provides additional clues that complement visual analysis:
- EXIF Data: If available, PlaceSpotter extracts details like:
- GPS coordinates
- Timestamps
- Camera orientation
- Device information
When GPS data aligns with recognizable landmarks in a photo, the system can confirm the location with greater certainty.
"PlaceSpotter helped me discover new locations for my photo shoots." - Stan S., Travel Photographer [1]
"The accuracy is incredible. It even identified barely recognizable locations perfectly." - Danielle P., Marketing Pro [1]
Privacy and Data Security
PlaceSpotter ensures user privacy by processing images securely and deleting them immediately after analysis.
| Data Type | Purpose | Privacy Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Elements | Analyzes landmarks and features | Deleted right after processing |
| GPS Data | Verifies precise coordinates | Encrypted during processing |
| Timestamps | Checks time zone and lighting | Stored anonymously |
Getting Started with PlaceSpotter
How to Upload and Get Results
Using PlaceSpotter is simple. The platform supports JPEG, PNG, and HEIC photo formats, with a maximum file size of 10MB. Here’s how to identify a location:
- Go to your PlaceSpotter dashboard.
- Drag and drop your photo.
- Wait for the analysis to complete.
- Check the detailed location results.
Once the analysis is done, PlaceSpotter deletes the original files, keeping only small previews for reference.
Plans and Costs
PlaceSpotter has options for different user needs:
| Plan | Monthly Price | Photo Limit | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 3 photos | Basic location data |
| Lite | $4.99 | 30 photos | Detailed location data, Priority support |
| Pro | $9.99 | 200 photos | Detailed location data, Priority support |
If you don’t need a monthly plan, credit packs are also available:
- 10 credits for $2.00 (10 photos)
- 100 credits for $15.00 (100 photos)
Credits are valid for 12 months from the purchase date.
Up next, explore how PlaceSpotter can enhance your travel logs, photography projects, or research efforts.
Ways to Use PlaceSpotter
PlaceSpotter is versatile and works for various purposes:
Travel Documentation
Pinpoint the locations of your travel photos to create detailed travel logs. The platform’s precise coordinate system makes it easy to track and document memories from past trips.
Photography Planning
Photographers can use PlaceSpotter to scout shoot locations. The detailed data helps identify ideal spots and understand environmental factors like lighting.
Research and Investigation
Researchers analyzing travel photos can extract accurate location data without affecting image quality. The platform supports various file formats, ensuring compatibility with different cameras and devices.
For the best results, use photos that meet these criteria:
- Clear and focused
- Under 10MB
- In a supported file format
- Include visible landmarks or unique features
Tips for Finding Photo Locations
Spotting Clues in Photos
You can figure out where a photo was taken by paying attention to both obvious and subtle details. Look closely at:
- Architecture: Styles of buildings and materials unique to certain regions.
- Street features: Things like streetlamps or public fixtures that have local designs.
- Natural elements: Terrain, types of plants, or geological markers that hint at geography.
- Regional details: Design trends or cultural elements that tie to specific areas.
Breaking down the foreground and background can help you pinpoint the location more accurately. Here's a quick guide:
| Element Type | What to Look For | What It Tells You |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Road markings, utility designs | Clues about the city or area |
| Landscape | Terrain, vegetation types | Geographic hints |
| Cultural | Design styles, public spaces | Regional identity |
| Weather | Seasonal signs, climate hints | Environmental context |
By examining these details, you can combine what you see with AI tools and manual research for better results.
Combining AI with Manual Research
PlaceSpotter's AI can give you a solid starting point, but manual research is key to refining those results. Here's how you can make the most of both:
- Use PlaceSpotter's AI to get initial location data.
- Cross-check the AI findings with interactive maps to match terrain.
- Verify architectural details using local business directories or resources.
- Use tools like SunCalc to figure out cardinal directions based on shadows.
- Search specialized databases to identify unique infrastructure elements.
- Compare vegetation patterns using seasonal satellite imagery.
- Pay attention to what’s missing in the photo to help narrow down possible locations.
Since metadata isn’t always reliable, blending PlaceSpotter's AI insights with manual verification ensures you get the most accurate and efficient results. This approach helps validate locations thoroughly without wasting time.
Privacy and Ethics
Keeping Data Private
Protecting your personal data is crucial, especially when it comes to photos and location details. Here are some steps to help you stay secure:
Photo Privacy Tips
- Use encryption to safeguard your uploads.
- Turn off your smartphone's automatic geotagging feature.
- Regularly delete metadata from photos before sharing them online.
Managing Existing Photos
Most smartphone photo apps offer tools to handle location data effectively. To maximize privacy, consider these actions:
| Action | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Remove EXIF Data | Deletes location coordinates | Prevents tracking of your location |
| Adjust Privacy Settings | Controls visibility of location info | Reduces risk of data exposure |
| Disable Auto-Geotagging | Stops future location embedding | Protects privacy by default |
These steps align with the ethical sharing practices discussed below.
Rules for Sharing Location Data
Responsible sharing of location details doesn’t just protect you - it also helps preserve communities and sensitive areas. For example, Horseshoe Bend in Arizona experienced a dramatic tourist increase, from a few thousand visitors in the 1990s to 1.5 million, partly due to geotagged social media posts [3].
Ethical Sharing Guidelines
"Use good judgment and be mindful of responsible geotagging in the first place."
- Christina Djossa, Writer and Audio Producer [3]
When sharing location information, keep these tips in mind:
- Tag broader areas instead of exact spots.
- Always get permission before photographing people.
- Think about privacy concerns, especially for children.
- Show respect for sacred or culturally significant sites.
- Be cautious about sharing details that might disturb wildlife habitats.
"By sharing the location of various flora and fauna, or reporting instances of littering and pollution, tourists can help local authorities and conservationists better understand ecological trends and challenges."
Digital Sovereignty
It’s important to respect the rights of Indigenous communities regarding how their cultural heritage is shared. Avoid photographing or posting images of cultural sites and ceremonies without permission. PlaceSpotter ensures these privacy and ethical standards are upheld while providing accurate location data.
Conclusion
AI-powered tools have made identifying locations from travel photos quicker and more precise. These advancements are proving useful for photographers, travelers, and investigators by improving accuracy and simplifying workflows.
How Modern Photo Location Tools Are Changing the Game
The integration of AI with metadata processing has transformed how photo locations are identified. Users frequently report impressive accuracy and greater efficiency in pinpointing and verifying locations, making these tools practical for both personal and professional needs.
The Importance of Balancing Technology with Privacy
While these tools achieve impressive results - like PIGEON's 95% accuracy in identifying countries [4] - privacy concerns remain a critical consideration. As Jay Stanley, Senior Policy Analyst at ACLU, explains:
"From a privacy point of view, your location can be a very sensitive set of information" [4]
The future of photo location technology relies on responsible use. Best practices include encrypting data, securing permissions, and carefully managing metadata to protect sensitive information.
Although these tools can analyze photos in seconds, it's up to users to ensure their data is secure and privacy rights are respected. By applying the recommendations in this guide, you can make the most of photo location tools while upholding ethical standards and protecting sensitive data.
FAQs
How can I achieve the best accuracy when using PlaceSpotter to identify locations in my travel photos?
To ensure the highest accuracy with PlaceSpotter, start by uploading clear, high-quality images. Photos with distinct landmarks, unique features, or visible signs provide better results. Avoid blurry or heavily edited images, as they may reduce accuracy.
Make sure the metadata (like EXIF data) is intact when uploading your photos. This includes GPS coordinates, timestamps, and camera settings, which can significantly enhance location identification. If your photo lacks metadata, focus on visual clues within the image, such as landmarks, street signs, or natural features, to help PlaceSpotter narrow down the location.
For optimal results, combine these strategies with PlaceSpotter's advanced tools, and double-check the suggestions provided to confirm the location matches your expectations.
How does PlaceSpotter ensure my privacy when analyzing photos?
PlaceSpotter takes privacy seriously and follows strict measures to protect your personal data when analyzing photos. Uploaded images are processed securely, and any sensitive information, such as location metadata, is handled with care to ensure it remains private.
Photos are only used for the purpose of providing geolocation insights and are not stored or shared without your consent. For added transparency, PlaceSpotter employs industry-standard encryption and complies with relevant data protection laws to safeguard your privacy.
Can PlaceSpotter help identify locations in old photos that don’t have metadata?
Yes, PlaceSpotter can assist in identifying locations in historical photos even if they lack metadata. Using advanced AI-powered geolocation tools, PlaceSpotter analyzes visual details within the image to provide reliable location insights.
While metadata like EXIF data can be helpful, PlaceSpotter's technology doesn’t rely on it, making it a great option for working with older or metadata-free images.